To host a Prefect server instance on Kubernetes, check out the prefect-server Helm chart.
- Workspaces: isolated environments to organize your flows, deployments, and flow runs
- Automations: configure triggers, actions, and notifications in response to real-time monitoring events
- Email notifications: send email alerts from Prefect’s servers based on automation triggers
- Service accounts: configure API access for running workers or executing flow runs on remote infrastructure
- Custom role-based access controls (RBAC): assign users granular permissions to perform activities within an account or workspace
- Single Sign-on (SSO): authentication using your identity provider
- Audit Logs: a record of user activities to monitor security and compliance
Prefect server installation notes
Your self-hosted server must meet the following requirements and configuration settings.SQLite
SQLite is not packaged with the Prefect installation. But most systems already have SQLite installed, and it is typically bundled with Python. If you host your own Prefect server instance with a SQLite database, certain Linux versions of SQLite can be problematic. Compatible versions include Ubuntu 22.04 LTS and Ubuntu 20.04 LTS. To confirm SQLite is installed, run:Use a self-signed SSL certificate
When using a self-signed SSL certificate, you need to configure your environment to trust the certificate. Add the certificate to your system bundle and point your tools to use that bundle by configuring theSSL_CERT_FILE environment variable.
If the certificate is not part of your system bundle, set the
PREFECT_API_TLS_INSECURE_SKIP_VERIFY to True to disable certificate verification altogether.
Proxies
Prefect supports communicating with proxies through environment variables. Whether you are using Prefect Cloud or hosting your own Prefect server instance, setHTTPS_PROXY and
SSL_CERT_FILE in your environment, and the underlying network libraries route Prefect’s requests appropriately.
Alternatively, the Prefect library connects to the API through any proxies you have listed in the HTTP_PROXY or
ALL_PROXY environment variables.
You may also use the NO_PROXY environment variable to specify which hosts should not pass through the proxy.
For more information about these environment variables, see the cURL documentation.
Run a local Prefect server
- Spin up a local Prefect server UI with the
prefect server startCLI command in the terminal:
- Open the URL for the Prefect server UI (http://127.0.0.1:4200 by default) in a browser.
- Shut down the Prefect server with ctrl + c in the terminal.
Configure a Prefect server instance
Go to your terminal session and run this command to set the API URL to point to a Prefect server instance:You must set the API server address,
PREFECT_API_URL, to use Prefect within a container, such as a Docker container.The Prefect database
The Prefect database persists data to track the state of your flow runs and related Prefect concepts, including:- Flow run and task run state
- Run history
- Logs
- Deployments
- Flow and task run concurrency limits
- Storage blocks for flow and task results
- Variables
- Artifacts
- Work pool status
- SQLite (default in Prefect): Recommended for lightweight, single-server deployments. SQLite requires essentially no setup.
- PostgreSQL: Best for connecting to external databases, but requires additional setup (such as Docker).
Prefect uses the
pg_trgmextension, so it must be installed and enabled.
Using the database
A local SQLite database is the default database and is configured upon Prefect installation. The database is located at~/.prefect/prefect.db by default.
To reset your database, run the CLI command:
Database settings
Prefect provides several settings for configuring the database. The default settings are:prefect config set.
Configure a PostgreSQL database
Connect Prefect to a PostgreSQL database by setting the following environment variable:- You have a username called
postgres - Your password is set to
yourTopSecretPassword - Your database runs on the same host as the Prefect server instance,
localhost - You use the default PostgreSQL port
5432 - Your PostgreSQL instance has a database called
prefect
Quickstart: configure a PostgreSQL database with Docker
Start a PostgreSQL instance to use as your Prefect database with the following command (which starts a Docker container running PostgreSQL):- Pulls the latest version of the official
postgresDocker image, which is compatible with Prefect. - Starts a container with the name
prefect-postgres. - Creates a database
prefectwith a userpostgresandyourTopSecretPasswordpassword. - Mounts the PostgreSQL data to a Docker volume called
prefectdbto provide persistence if you ever have to restart or rebuild that container.
Confirm your PostgreSQL database configuration
Inspect your Prefect profile to confirm that the environment variable has been properly set:In-memory database
To use an in-memory SQLite database, set the following environment variable:Migrations
Prefect uses Alembic to manage database migrations. Alembic is a database migration tool to use with the SQLAlchemy Database Toolkit for Python. Alembic provides a framework for generating and applying schema changes to a database. Apply migrations to your database with the following commands: To upgrade:-r flag to specify a specific migration version to upgrade or downgrade to.
For example, to downgrade to the previous migration version, run:
base revision.
See the contributing docs to create new database migrations.
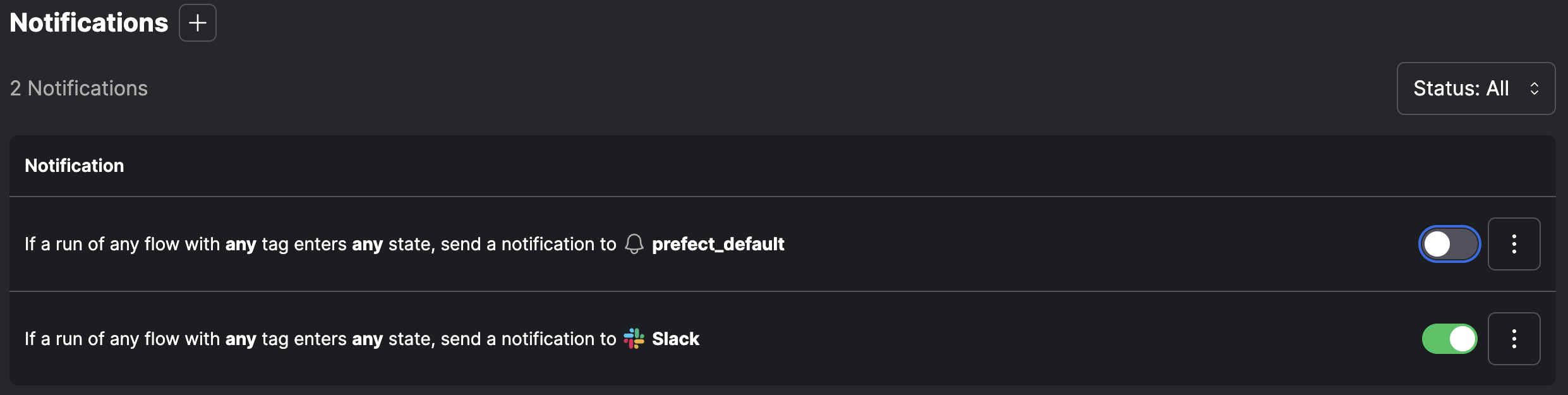
Notifications
Prefect Cloud gives you access to a hosted platform with Workspace and User controls, Events, and Automations. Prefect Cloud has an option for automation notifications. The more limited Notifications option is provided for the self-hosted Prefect server. Notifications enable you to set up alerts that are sent when a flow enters any state you specify. When your flow and task runs changes state, Prefect notes the state change and checks whether the new state matches any notification policies. If it does, a new notification is queued. Prefect supports sending notifications through:- Custom webhook
- Discord webhook
- Mattermost webhook
- Microsoft Teams webhook
- Opsgenie webhook
- PagerDuty webhook
- Sendgrid email
- Slack webhook
- Twilio SMS
Notifications in Prefect CloudPrefect Cloud uses the robust Automations interface to
enable notifications related to flow run state changes and work pool status.
Configure notifications
To configure a notification in a Prefect server, go to the Notifications page and select Create Notification or the + button.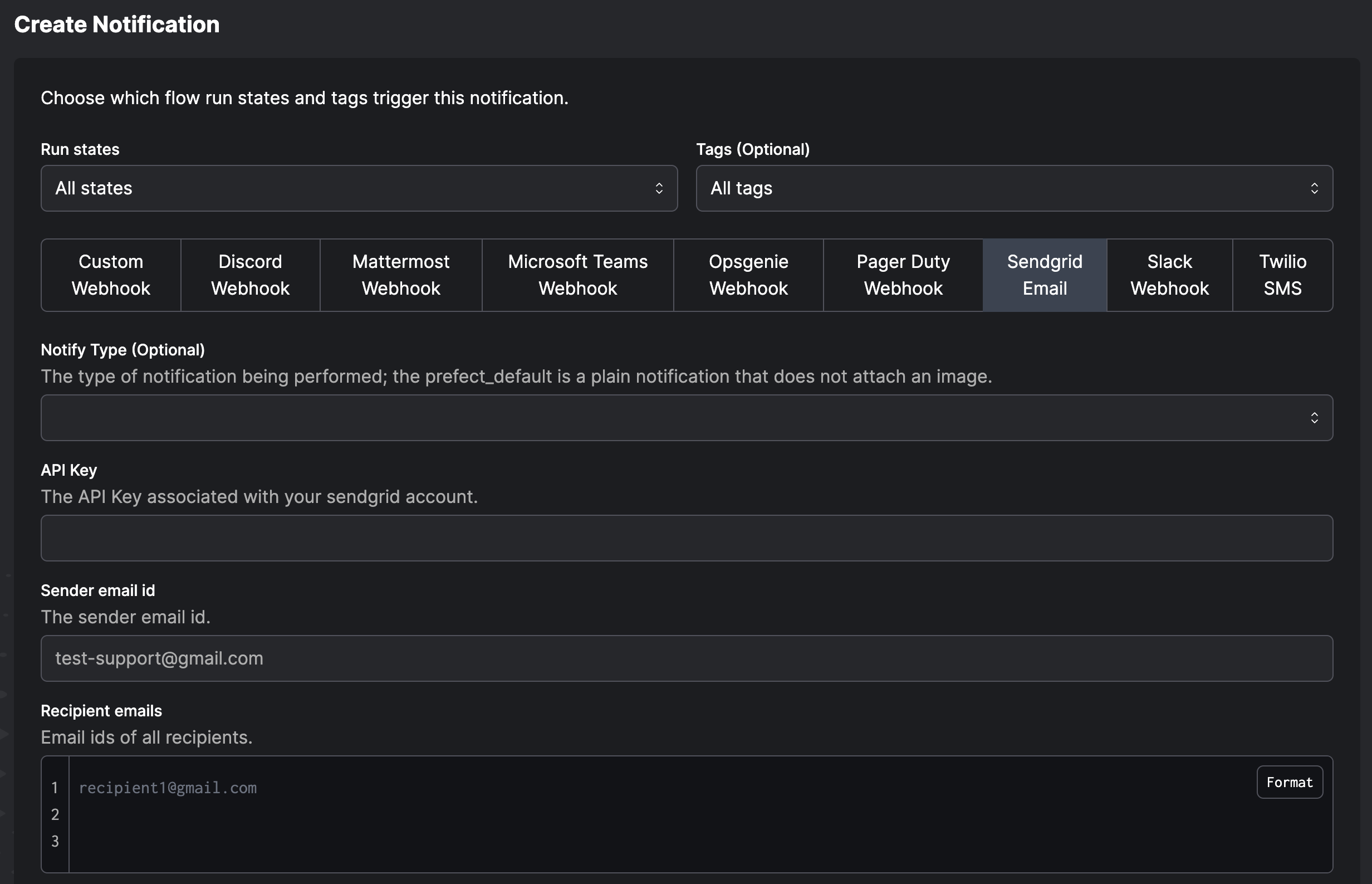 You can choose:
You can choose:
- Which run states should trigger a notification
- Tags to filter which flow runs are covered by the notification
- Whether to send an email, a Slack message, Microsoft Teams message, or use another services
daily-etl tag fails, the notification will read:
If a run of any flow with daily-etl tag enters a failed state, send a notification to my-slack-webhookWhen the conditions of the notification are triggered, you’ll receive a message:
The fuzzy-leopard run of the daily-etl flow entered a failed state at 22-06-27 16:21:37 EST.On the Notifications page you can pause, edit, or delete any configured notification.