Prefect is an orchestration and observability platform that empowers developers to build and scale code quickly.
In this quickstart, you will use Prefect to convert the following Python script to a schedulable, observable, resilient, and deployable workflow in minutes:
import httpx
def get_repo_info():
"""Fetch statistics about the Prefect repository"""
url = "https://api.github.com/repos/PrefectHQ/prefect"
response = httpx.get(url)
repo = response.json()
print("PrefectHQ/prefect repository statistics 🤓:")
print(f"Stars 🌠 : {repo['stargazers_count']}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
get_repo_info()
Install Prefect
Install Prefect.
pip install -U prefect --pre
Connect to Prefect’s API
Connect to the Prefect API, either Prefect Cloud hosted by us, or a local Prefect server instance:
Prefect Cloud
Local server
-
Head to https://app.prefect.cloud/ and sign in or create a forever-free Prefect Cloud account.
-
Log in to Prefect Cloud from your development environment:
-
Choose Log in with a web browser and click the Authorize button in the browser window that opens.
Your CLI is now authenticated with your Prefect Cloud account through a locally-stored API key that expires in 30 days.If you have any issues with browser-based authentication, see the Prefect Cloud docs to learn how to authenticate with a manually created API key.
-
Ensure your current profile isn’t authenticated to Prefect Cloud:
-
Start a local API server:
-
Open the Prefect dashboard in your browser at http://localhost:4200.
Convert your script to a Prefect flow
The easiest way to convert a Python script into a workflow is to add a @flow decorator to the script’s entrypoint, the Python function that runs first.
Flows are containers for workflow logic as code.
They’re the core observable, orchestrated, deployable units of work in Prefect.
Adding @task decorators to the functions called by the flow converts them to tasks.
Tasks receive metadata about upstream dependencies and the state of those dependencies before they run.
Prefect will record these dependencies and states as it orchestrates these tasks when they run.
import httpx # an HTTP client library and dependency of Prefect
from prefect import flow, task
@task(retries=2)
def get_repo_info(repo_owner: str, repo_name: str):
"""Get info about a repo - will retry twice after failing"""
url = f"https://api.github.com/repos/{repo_owner}/{repo_name}"
api_response = httpx.get(url)
api_response.raise_for_status()
repo_info = api_response.json()
return repo_info
@task
def get_contributors(repo_info: dict):
"""Get contributors for a repo"""
contributors_url = repo_info["contributors_url"]
response = httpx.get(contributors_url)
response.raise_for_status()
contributors = response.json()
return contributors
@flow(log_prints=True)
def repo_info(repo_owner: str = "PrefectHQ", repo_name: str = "prefect"):
"""
Given a GitHub repository, logs the number of stargazers
and contributors for that repo.
"""
repo_info = get_repo_info(repo_owner, repo_name)
print(f"Stars 🌠 : {repo_info['stargazers_count']}")
contributors = get_contributors(repo_info)
print(f"Number of contributors 👷: {len(contributors)}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
repo_info()
The log_prints=True argument provided to the @flow decorator logs output from print statements within the function.
Run your flow
Run your Prefect flow just as you would a Python script:
Prefect automatically tracks the state of the flow run and logs the output in the UI and CLI.
14:28:31.099 | INFO | prefect.engine - Created flow run 'energetic-panther' for flow 'repo-info'
14:28:31.100 | INFO | Flow run 'energetic-panther' - View at https://app.prefect.cloud/account/123/workspace/abc/flow-runs/flow-run/xyz
14:28:32.178 | INFO | Flow run 'energetic-panther' - Created task run 'get_repo_info-0' for task 'get_repo_info'
14:28:32.179 | INFO | Flow run 'energetic-panther' - Executing 'get_repo_info-0' immediately...
14:28:32.584 | INFO | Task run 'get_repo_info-0' - Finished in state Completed()
14:28:32.599 | INFO | Flow run 'energetic-panther' - Stars 🌠 : 13609
14:28:32.682 | INFO | Flow run 'energetic-panther' - Created task run 'get_contributors-0' for task 'get_contributors'
14:28:32.682 | INFO | Flow run 'energetic-panther' - Executing 'get_contributors-0' immediately...
14:28:33.118 | INFO | Task run 'get_contributors-0' - Finished in state Completed()
14:28:33.134 | INFO | Flow run 'energetic-panther' - Number of contributors 👷: 30
14:28:33.255 | INFO | Flow run 'energetic-panther' - Finished in state Completed('All states completed.')
Create a work pool
Running a flow locally is a good start, but you should use a remote destination for production flows.
A work pool is the most common way to do this.
Prefect Cloud
Local server
Deploy your flow to Cloud using a managed work pool.
-
Create a managed work pool:
prefect work-pool create my-work-pool --type prefect:managed
-
View your new work pool on the Work Pools page of the UI.
Deploy your flow to your local server using a Process type work pool.
-
Create a Process type work pool:
prefect work-pool create --type process my-work-pool
-
Verify that the work pool exists:
-
Start a worker in the work pool:
prefect worker start --pool my-work-pool
Deploy and schedule your flow
A deployment is used to determine when, where, and how a flow function should run.
Deployments elevate flows to remotely configurable entities that have their own API.
-
Create a deployment script:
from prefect import flow
# Source for the code to deploy (here, a GitHub repo)
SOURCE_REPO="https://github.com/prefecthq/demos.git"
if __name__ == "__main__":
flow.from_source(
source=SOURCE_REPO,
entrypoint="my_gh_workflow.py:repo_info", # Specific flow to run
).deploy(
name="my-first-deployment",
work_pool_name="my-work-pool", # Work pool target
cron="0 1 * * *", # Cron schedule (1am every day)
)
-
Run the script to create the deployment:
python create_deployment.py
Successfully created/updated all deployments!
______________________________________________________
| Deployments |
______________________________________________________
| Name | Status | Details |
______________________________________________________
| repo-info/my-first-deployment | applied | |
______________________________________________________
-
Schedule a run for the deployment:
prefect deployment run 'repo-info/my-first-deployment'
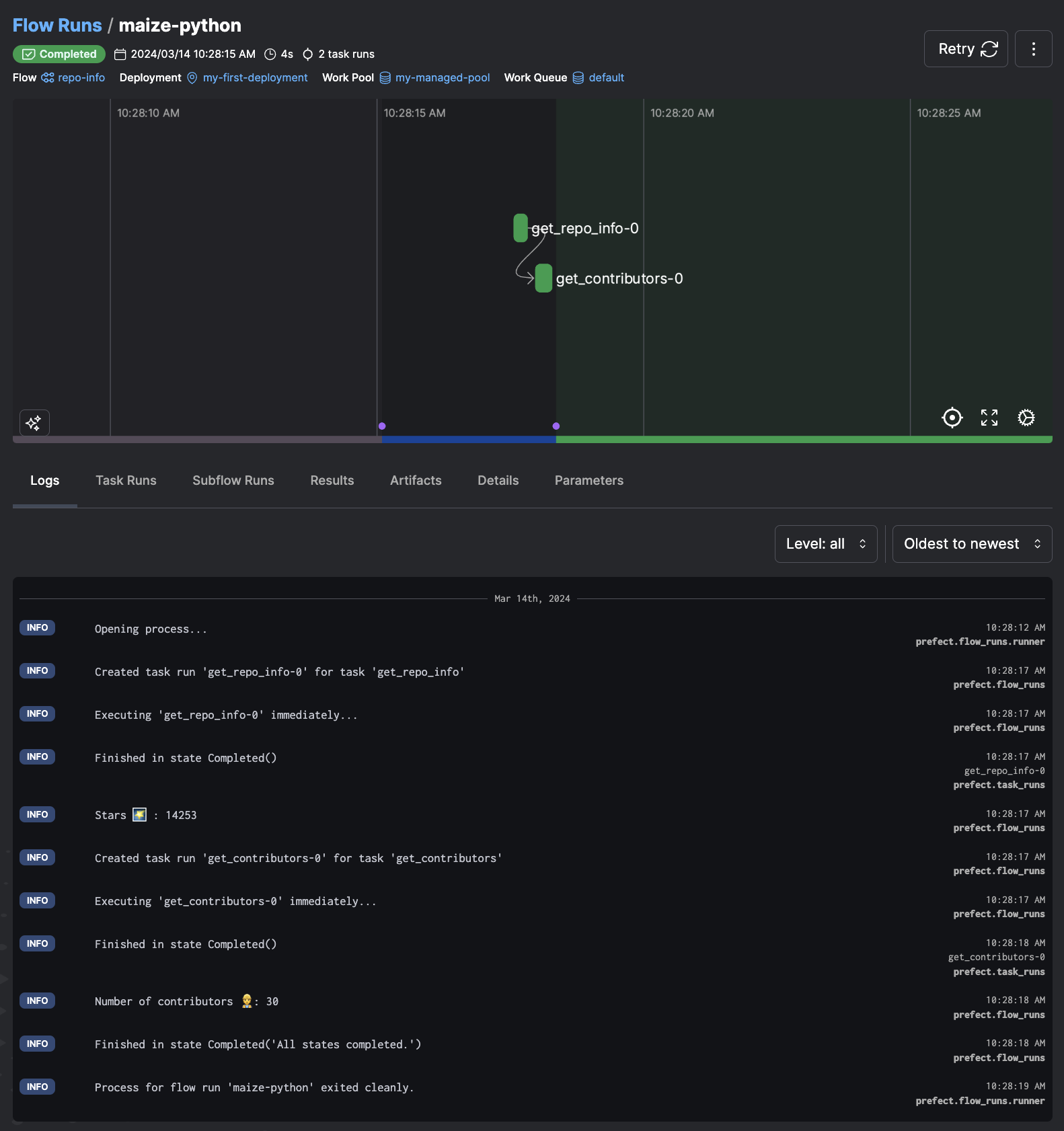
-
When you’re done, click the More > Delete button on the Deployments page to stop further scheduled runs.
Next steps
You’ve seen how to move from a Python script to a scheduled, observable, remotely orchestrated workflow with Prefect.
Now considering reading:
Need help? Book a meeting with a Prefect Product Advocate to get your questions answered. 

