submits flow runs to serverless infrastructure directly, depending on your configuration.
Work pool-based deploymentsThis guide focuses on work pools and workers. For guidance on work pool-based deployments, see
Deploy flows to work pools and workers
.
Work pool overview
Work pools organize work for execution. Work pools have types corresponding to the infrastructure to execute the flow code, as well as the delivery method of work to that environment. Pull work pools require workers to poll the work pool for flow runs to execute. Push work pools submit runs directly to your serverless infrastructure providers such as Google Cloud Run, Azure Container Instances, and AWS ECS without the need for an agent or worker. Managed work pools are administered by Prefect and handle the submission and execution of code on your behalf. Users can control aspects of work pool behavior, such as how many runs the pool allows to run concurrently. You can modify these options at any time, and any workers requesting work for a specific pool only see matching flow runs.Work pool configuration
You can configure work pools by using any of the following:- Prefect UI
- Prefect CLI commands
- Prefect REST API
- Terraform provider for Prefect Cloud
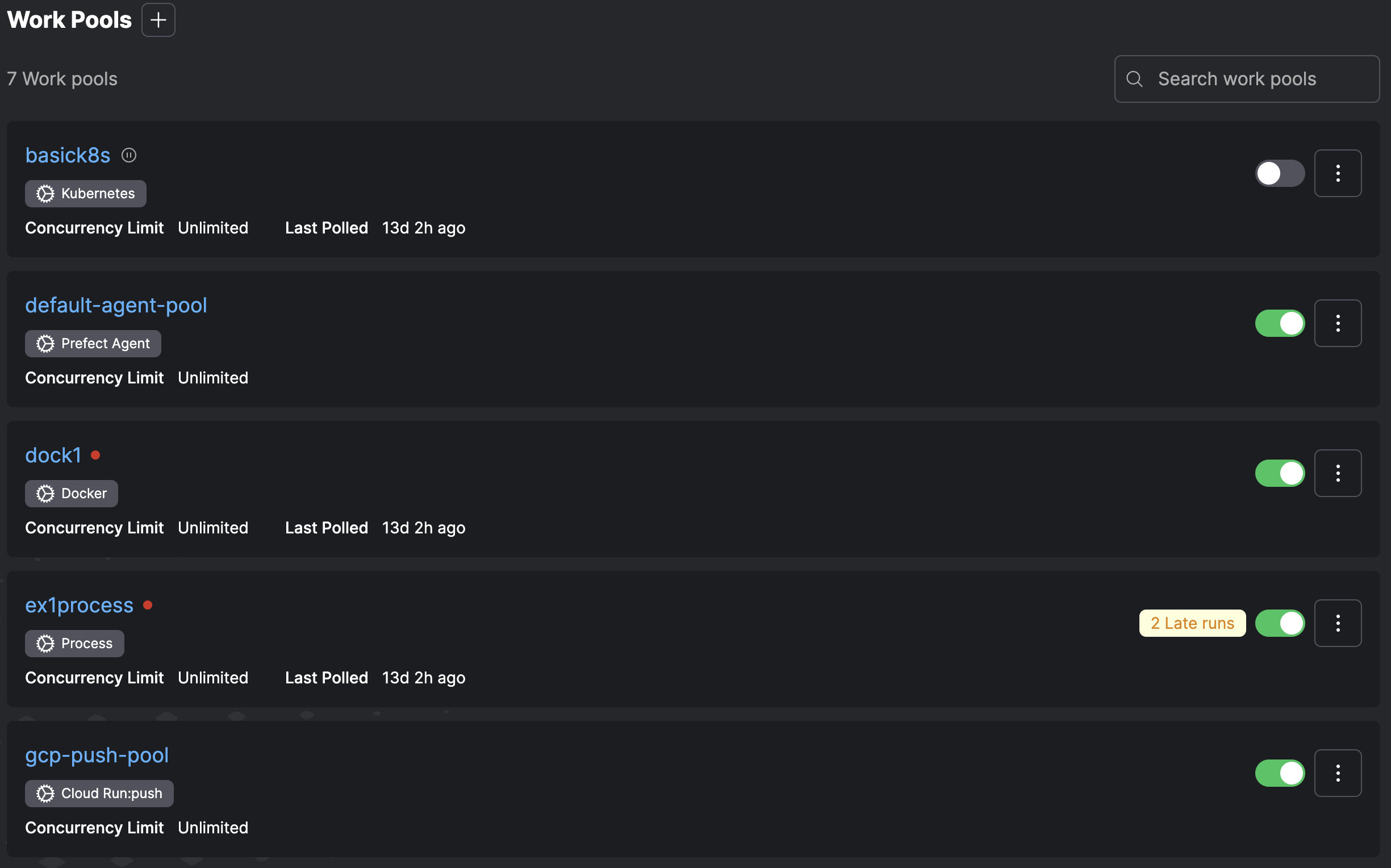 You can pause a work pool from this page by using the toggle.
Select the + button to create a new work pool. You can specify the details for work served by this work pool.
To create a work pool through the Prefect CLI, use the
You can pause a work pool from this page by using the toggle.
Select the + button to create a new work pool. You can specify the details for work served by this work pool.
To create a work pool through the Prefect CLI, use the prefect work-pool create command:
NAME is a required, unique name for the work pool.
Optional configuration parameters to filter work on the pool include:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
--paused | If provided, the work pool is created in a paused state. |
--type | The type of infrastructure that can execute runs from this work pool. |
--set-as-default | Whether to use the created work pool as the local default for deployment. |
--base-job-template | The path to a JSON file containing the base job template to use. If unspecified, Prefect uses the default base job template for the given worker type. |
test-pool, run:
Work pool types
If you don’t use the--type flag to specify an infrastructure type, you are prompted to select from the following options:
- Prefect Cloud
- Prefect server instance
| Infrastructure Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Execute flow runs as subprocesses on a worker. Works well for local execution when first getting started. |
| AWS Elastic Container Service | Execute flow runs within containers on AWS ECS. Works with EC2 and Fargate clusters. Requires an AWS account. |
| Azure Container Instances | Execute flow runs within containers on Azure’s Container Instances service. Requires an Azure account. |
| Docker | Execute flow runs within Docker containers. Works well for managing flow execution environments through Docker images. Requires access to a running Docker daemon. |
| Google Cloud Run | Execute flow runs within containers on Google Cloud Run. Requires a Google Cloud Platform account. |
| Google Cloud Run V2 | Execute flow runs within containers on Google Cloud Run (V2 API). Requires a Google Cloud Platform account. |
| Google Vertex AI | Execute flow runs within containers on Google Vertex AI. Requires a Google Cloud Platform account. |
| Kubernetes | Execute flow runs within jobs scheduled on a Kubernetes cluster. Requires a Kubernetes cluster. |
| Google Cloud Run - Push | Execute flow runs within containers on Google Cloud Run. Requires a Google Cloud Platform account. Flow runs are pushed directly to your environment, without the need for a Prefect worker. |
| AWS Elastic Container Service - Push | Execute flow runs within containers on AWS ECS. Works with existing ECS clusters and serverless execution through AWS Fargate. Requires an AWS account. Flow runs are pushed directly to your environment, without the need for a Prefect worker. |
| Azure Container Instances - Push | Execute flow runs within containers on Azure’s Container Instances service. Requires an Azure account. Flow runs are pushed directly to your environment, without the need for a Prefect worker. |
| Modal - Push | Execute flow runs on Modal. Requires a Modal account. Flow runs are pushed directly to your Modal workspace, without the need for a Prefect worker. |
| Prefect Managed | Execute flow runs within containers on Prefect managed infrastructure. |
--set-as-default flag.
Which results in output similar to the following:
prefect work-pool update command:
NAME is the name of the work pool to update.
Optional configuration parameters you can specify to update the work pool include:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
--base-job-template | The path to a JSON file containing the base job template to use. If unspecified, Prefect uses the default base job template for the given worker type. |
--description | A description of the work pool. |
--concurrency-limit | The maximum number of flow runs to run simultaneously in the work pool. |
Base job template
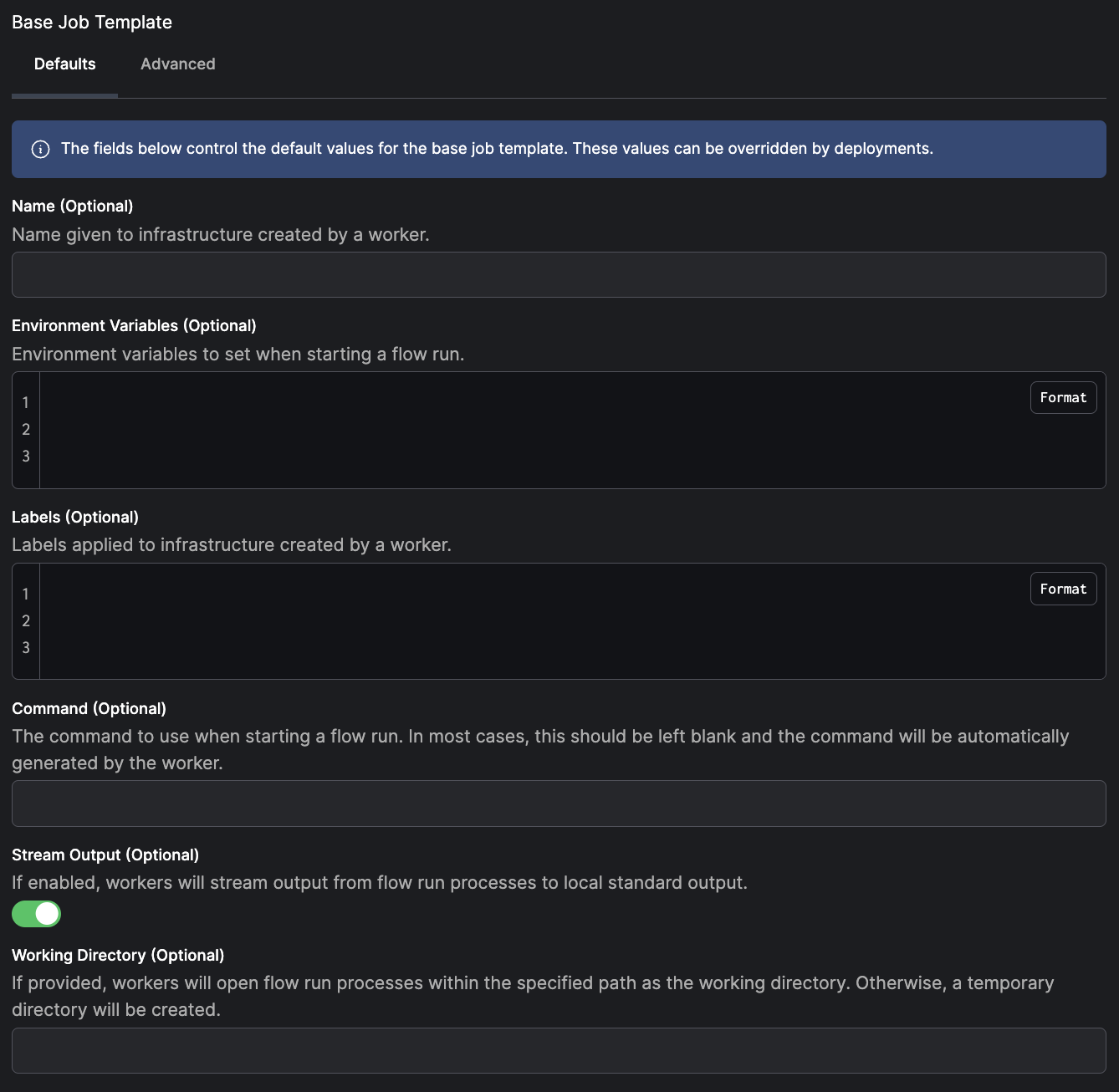
Each work pool has a base job template that allows the customization of the behavior of the worker executing flow runs from the work pool. The base job template acts as a contract defining the configuration passed to the worker for each flow run and the options available to deployment creators to customize worker behavior per deployment. A base job template comprises ajob_configuration section and a variables section.
The variables section defines the fields available that are customized per deployment. The variables section follows the
OpenAPI specification, which allows work pool creators to place limits on provided values
(for example, type, minimum, maximum).
The job configuration section takes the values provided in the variables section and translates them into a configuration.
It then gives this configuration to a worker when it executes a flow run.
The values in the job_configuration can use placeholders to reference values provided in the variables section.
Declare placeholders with double curly braces, for example, {{ variable_name }}. You can also hard-code job_configuration values.
Each worker type is configured with a default base job template, making it easy to start with a work pool.
The default base template defines values that pass to every flow run, but you can override on a per-deployment or per-flow run basis.
For example, if you create a process work pool named ‘above-ground’ through the CLI:
 For a
For a process work pool with the default base job template:
- set environment variables for spawned processes
- set the working directory to execute flows
- control whether the flow run output is streamed to workers’ standard output
deployments.work_pool.job_variables section of a prefect.yaml file or in the job_variables
argument of a Python flow.deploy method.
For example, to turn off streaming output for a specific deployment, add the following to your prefect.yaml:
View work pools
At any time, users can see and edit configured work pools in the Prefect UI. To view work pools with the Prefect CLI, you can:
To view work pools with the Prefect CLI, you can:
- List (
ls) all available pools - Inspect (
inspect) the details of a single pool - Preview (
preview) scheduled work for a single pool
prefect work-pool ls lists all configured work pools for the server.
prefect work-pool inspect provides all configuration metadata for a specific work pool by ID.
prefect work-pool preview displays scheduled flow runs for a specific work pool by ID for the upcoming hour. The optional --hours flag lets you specify the number of hours to look ahead.
Work pool status
Work pools have three statuses:READY: A work pool has at least one online worker sending heartbeats to the work pool.NOT_READY: A work pool has no online workers.PAUSED: You can place a work pool in a paused status manually or through an automation. When a paused work pool is unpaused, it is reassigned the appropriate status based on whether any workers are sending heartbeats.
Pause and delete work pools
You can pause a work pool at any time to stop the delivery of work to workers. Workers will not receive any work when polling a paused pool. To pause a work pool through the Prefect CLI, use theprefect work-pool pause command:
prefect work-pool resume command with the work pool name.
To delete a work pool through the Prefect CLI, use the prefect work-pool delete command with the work pool name.
Manage concurrency
Each work pool can optionally restrict concurrent runs of matching flows. For example, a work pool with a concurrency limit of 5 only releases new work if less than five matching runs are in aRunning or Pending state. If three runs are Running or Pending, polling the pool for work only results in two new runs—
even if there are many more available, to ensure that the concurrency limit is not exceeded.
When using the prefect work-pool Prefect CLI command to configure a work pool, the following subcommands set concurrency limits:
set-concurrency-limitsets a concurrency limit on a work poolclear-concurrency-limitclears any concurrency limits from a work pool
Work queues
Work queues offer advanced control over how runs are executed. Each work pool has a “default” queue work is sent to by default. Add additional queues to a work pool to enable greater control over work delivery through fine-grained priority and concurrency. Each work queue has a priority indicated by a unique positive integer. Lower numbers take greater priority in the allocation of work. Accordingly, you can add new queues without changing the rank of the higher-priority queues (for example,the queue with priority
1 will always be the highest priority).
Work queues can also have their own concurrency limits. Each queue is also subject to the global work pool concurrency limit,
which cannot be exceeded.
Queue priority
Together, work queue priority and concurrency enable precise control over work. For example, a pool may have three queues:- a “low” queue with priority
10and no concurrency limit - a “high” queue with priority
5and a concurrency limit of3 - a “critical” queue with priority
1and a concurrency limit of1
Queue concurrency limits
Priority determines the order of flow runs submitted for execution. If all flow runs are capable of being executed with no limitation due to concurrency or otherwise, priority is still used to determine order of submission, but there is no impact to execution. If not all flow runs can execute, usually as a result of concurrency limits, priority determines which queues receive precedence to submit runs for execution.Precise control with priority and concurrency
Priority for flow run submission proceeds from the highest priority to the lowest priority. In the previous example, all work from the “critical” queue (priority 1) is submitted, before any work is submitted from “high” (priority 5). Once all work is submitted from priority queue “critical”, work from the “high” queue begins submission. If new flow runs are received on the “critical” queue while flow runs are still in scheduled on the “high” and “low” queues, flow run submission goes back to ensuring all scheduled work is first satisfied. This happens from the highest priority queue, until it is empty, in waterfall fashion.Worker overview
Workers are lightweight polling services that retrieve scheduled runs from a work pool and execute them. Workers each have a type corresponding to the execution environment to submit flow runs to. Workers can only poll work pools that match their type. As a result, when deployments are assigned to a work pool, you know in which execution environment scheduled flow runs for that deployment will run.Worker types
Below is a list of available worker types. Most worker types require installation of an additional package.| Worker Type | Description | Required Package |
|---|---|---|
process | Executes flow runs in subprocesses | |
kubernetes | Executes flow runs as Kubernetes jobs | prefect-kubernetes |
docker | Executes flow runs within Docker containers | prefect-docker |
ecs | Executes flow runs as ECS tasks | prefect-aws |
cloud-run | Executes flow runs as Google Cloud Run jobs | prefect-gcp |
vertex-ai | Executes flow runs as Google Cloud Vertex AI jobs | prefect-gcp |
azure-container-instance | Execute flow runs in ACI containers | prefect-azure |
Worker options
Workers poll for work from one or more queues within a work pool. If the worker references a work queue that doesn’t exist, it is created automatically. The worker CLI infers the worker type from the work pool. Alternatively, you canspecify the worker type explicitly. If you supply the worker type to the worker CLI, a work pool is created automatically if it doesn’t exist (using default job settings). Configuration parameters you can specify when starting a worker include:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
--name, -n | The name to give to the started worker. If not provided, a unique name will be generated. |
--pool, -p | The work pool the started worker should poll. |
--work-queue, -q | One or more work queue names for the worker to pull from. If not provided, the worker pulls from all work queues in the work pool. |
--type, -t | The type of worker to start. If not provided, the worker type is inferred from the work pool. |
--prefetch-seconds | The amount of time before a flow run’s scheduled start time to begin submission. Default is the value of PREFECT_WORKER_PREFETCH_SECONDS. |
--run-once | Only run worker polling once. By default, the worker runs forever. |
--limit, -l | The maximum number of flow runs to start simultaneously. |
--with-healthcheck | Start a healthcheck server for the worker. |
--install-policy | Install policy to use workers from Prefect integration packages. |
kubernetes, the worker deploys flow runs to a Kubernetes cluster.
Prefect must be installed in any environment (for example, virtual environment, Docker container) where you intend to run the worker or
execute a flow run.
Worker status
Workers have two statuses:ONLINE and OFFLINE. A worker is online if it sends regular heartbeat messages to the Prefect API.
If a worker misses three heartbeats, it is considered offline. By default, a worker is considered offline a maximum of 90 seconds
after it stopped sending heartbeats, but you can configure the threshold with the PREFECT_WORKER_HEARTBEAT_SECONDS setting.
Start a worker
Use theprefect worker start CLI command to start a worker. You must pass at least the work pool name.
If the work pool does not exist, it will be created if the --type flag is used.
--type flag:
--limit flag.
For example, to limit a worker to five concurrent flow runs:
Configure prefetch
By default, the worker submits flow runs a short time (10 seconds) before they are scheduled to run. This allows time for the infrastructure to be created so the flow run can start on time. In some cases, infrastructure takes longer than 10 seconds to start the flow run. You can increase the prefetch with the--prefetch-seconds option or the PREFECT_WORKER_PREFETCH_SECONDS setting.
If this value is more than the amount of time it takes for the infrastructure to start, the flow run will wait until its
scheduled start time.
Polling for work
Workers poll for work every 15 seconds by default. You can configure this interval in your profile settings with thePREFECT_WORKER_QUERY_SECONDS setting.
Install policy
The Prefect CLI can install the required package for Prefect-maintained worker types automatically. Configure this behavior with the--install-policy option. The following are valid install policies:
| Install Policy | Description |
|---|---|
always | Always install the required package. Updates the required package to the most recent version if already installed. |
if-not-present | Install the required package if it is not already installed. |
never | Never install the required package. |
prompt | Prompt the user to choose whether to install the required package. This is the default install policy. |
If prefect worker start is run non-interactively, the prompt install policy behaves the same as never. |
Additional resources
See how to daemonize a Prefect worker. See more information on overriding a work pool’s job variables.Benefits of work pools
Work pools are a bridge between the Prefect orchestration layer and infrastructure for flow runs that can be dynamically provisioned. To transition from persistent infrastructure to dynamic infrastructure, useflow.deploy instead of flow.serve.
The primary reason to use work pools is for dynamic infrastructure provisioning and configuration.
For example, you might have a workflow that has expensive infrastructure requirements and is run infrequently.
In this case, you don’t want an idle process running within that infrastructure.
Deployment definition methods differ slightly for work poolsWhen you use work-pool-based execution, you define deployments differently.
Configure deployments for workers with
deploy, which requires additional configuration.
You cannot use a deployment created with serve with a work pool.- Configure default infrastructure configurations on your work pools that all jobs inherit and can override.
- Allow platform teams to use work pools to expose opinionated (and enforced) interfaces to the infrastructure that they oversee.
- Allow work pools to prioritize (or limit) flow runs through the use of work queues.
Set up a work pool
Prefect CloudThis tutorial uses Prefect Cloud to deploy flows to work pools.
Managed execution and push work pools are available in Prefect Cloud only.
Create a Prefect Managed work pool
Run the following command to set up a work pool namedmy-managed-pool of type prefect:managed.
my-managed-pool in the output list.
Navigate to the Work Pools tab in the UI and verify that my-managed-pool is listed.
Select Edit from the three-dot menu on the work pool card to view the details of your work pool.
Work pools specify configuration to dynamically provision infrastructure for flow runs.
For example, you can specify additional Python packages or environment variables for all deployments that use this work pool.
Individual deployments can override the work pool configuration.
Now that you set up your work pool, you can deploy a flow to it. Deploy your test flow to my-managed-pool.
Create the deployment
From the previous steps, you now have:- A flow
- A work pool
repo_info.py file to create a deployment in Prefect Cloud with these modifications:
- Change
flow.servetoflow.deploy - Tell
flow.deploywhich work pool to deploy to
repo_info.py looks like this:
repo_info.py
from_source method, specify the source of your flow code.
In the deploy method, specify the name of your deployment and the name of the work pool you created earlier.
This example uses a GitHub repository for remote storage, but you can also use a Docker image.
You can also store your flow code in cloud provider storage such as AWS S3, or within a different git-based cloud provider
such as GitLab or Bitbucket.
In the example above, you stored your code in a GitHub repository.
If you make changes to the flow code, you must push those changes to your own GitHub account and update the
source argument
of from_source to point to your repository.Schedule a deployment run
You’re ready to submit a flow-run to the work pool. Run the deployment from the CLI (or the UI):See the Managed Execution guide for more details. For more control over the infrastructure that your flows run on, we recommend Prefect Cloud’s push work pools.
Push work pools with automatic infrastructure provisioning
Serverless push work pools scale infinitely and provide more configuration options than Prefect Managed work pools. Prefect provides push work pools for AWS ECS on Fargate, Azure Container Instances, Google Cloud Run, and Modal. Push work pools require a cloud provider account with certain permissions. This example uses GCP.Create a push work pool with automatic infrastructure provisioning
Prerequisites:- Install the gcloud CLI and authenticate with your GCP project.
- If you already have the gcloud CLI installed, update to the latest version with
gcloud components update. - The following permissions in your GCP project:
- resourcemanager.projects.list
- serviceusage.services.enable
- iam.serviceAccounts.create
- iam.serviceAccountKeys.create
- resourcemanager.projects.setIamPolicy
- artifactregistry.repositories.create
- Docker installed to build and push images to your registry. Install Docker.
my-cloud-run-pool of type cloud-run:push, run:
--provision-infra flag allows you to select a GCP project for your work pool and automatically configure it to execute
flows through Cloud Run.
In your GCP project, this command activates the Cloud Run API, and creates a service account and a key (if they don’t already exist).
In your Prefect workspace, this command creates a GCPCredentials block
for storing the service account key.
Here’s an abbreviated example output from running the command:
example_deploy_script.py
<region>-docker.pkg.dev/<project>/<repository-name>/my-image:latest
and pushes it to your repository. Make sure you have Docker running locally before running this script.
You only need to include an object of the DockerImage class with the argument platform="linux/amd64 if you’re
building your image on a machine with an ARM-based processor.
Otherwise, you can pass image="my-image:latest" to deploy.
Next steps
Thecron argument schedules the deployment to run at 1:00 AM every day.
See the schedules guide for more information on scheduling options.
See the Push Work Pool guide for more details and example commands for each
cloud provider.
If you need more control over your infrastructure, want to run your workflows in Kubernetes, or are running a self-hosted Prefect
server instance, see the Workers guide. You will learn how
to use work pools that rely on a worker and customize Docker images for container-based infrastructure.
