- named, mutable values of any JSON type
- scoped to a Prefect server instance or a single workspace in Prefect Cloud
- meant for values with infrequent writes and frequent reads (but you can create or modify variables at any time)
- cacheable for quicker retrieval
- most commonly loaded during flow runtime (but you can load them in other contexts to pass configuration information to Prefect configuration files, such as deployment steps)
Manage variables
Create, read, edit, and delete variables through the Prefect UI, API, and CLI. Names must adhere to these traditional variable naming conventions:- Have no more than 255 characters
- Only contain lowercase alphanumeric characters ([a-z], [0-9]) or underscores (_). Spaces are not allowed.
- Be unique
Through the Prefect UI
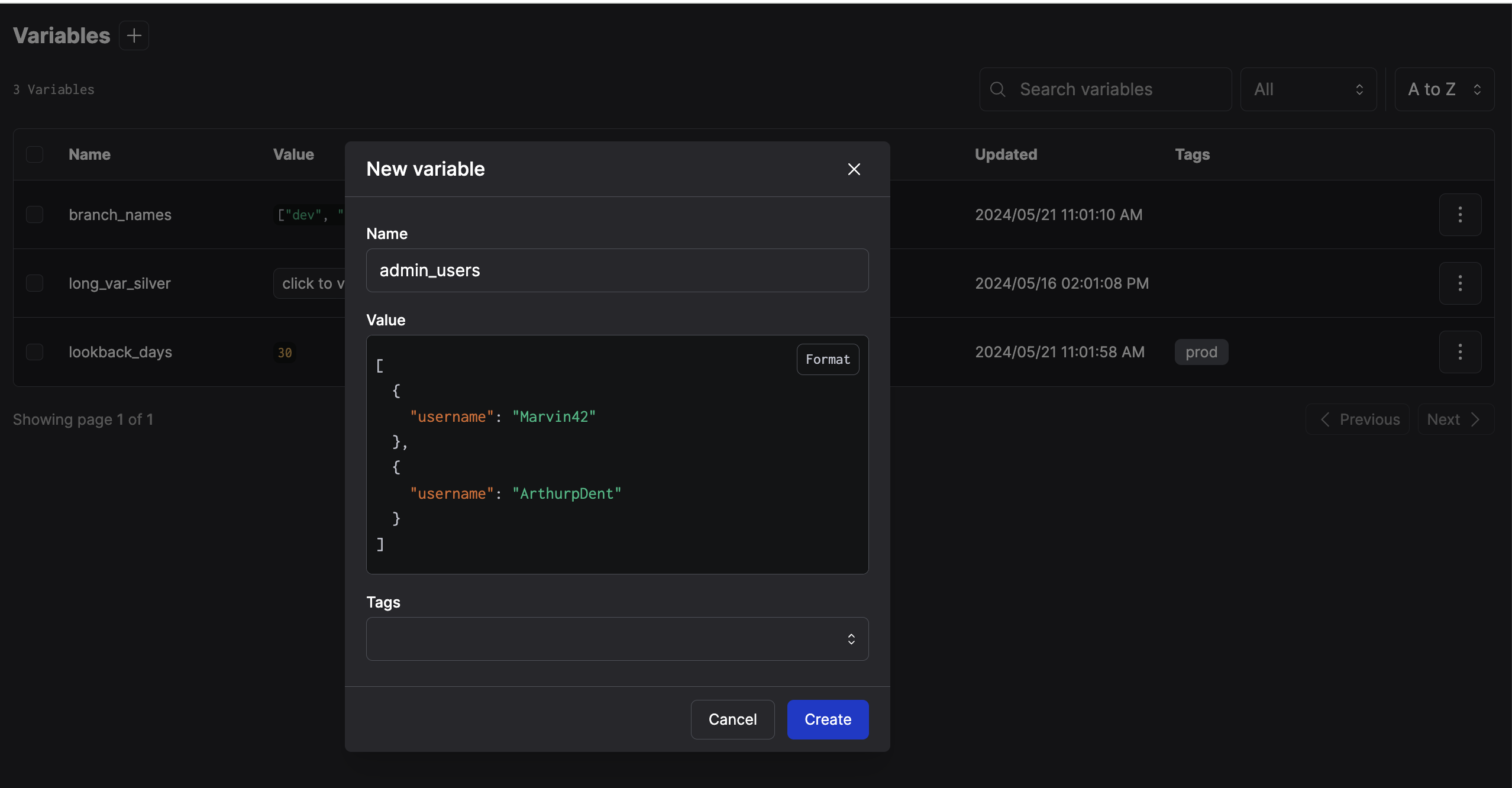
View all the variables in your Prefect server instance or Prefect Cloud workspace in the Variables page of the Prefect UI. Both the name and value of all variables are visible to anyone with access to the server or workspace. To create a new variable:- Select the + button next to the header of the Variables page.
- Enter the name and value of the variable.
Through the REST API
You can create and delete variables through the REST API. You can also set and get variables through the API with either the variable name or ID. See the REST reference for more information.Through the CLI
prefect variable setcreates or updates a variable.prefect variable getretrieves a variable’s value.prefect variable unsetdeletes a variable.prefect variable lslists all variables.prefect variable inspectshows a variable’s details.
Accessing variables
In addition to the UI and API, you can reference variables in code and in certain Prefect configuration files.In Python code
You can interact with variables through the Python SDK using theget, set, and unset methods.
Outside of a flow or task, these methods are always invoked asynchronously.
In an asynchronous context:
flow or task, variables should be invoked synchronously or asynchronously
depending on whether the current context is synchronous or asynchronous.
In a synchronous context:
In prefect.yaml deployment steps
In .yaml files, variables are denoted by quotes and double curly brackets, such as:
"{{ prefect.variables.my_variable }}". Use variables to templatize deployment steps by
referencing them in the prefect.yaml file that creates the deployments.
For example, you can pass in a variable to specify a branch for a git repo in a deployment pull step:
deployment_branch variable is evaluated at runtime for the deployed flow,
allowing changes to variables used in a pull action without updating a deployment directly.
